EDUCATION
Come back to this page anytime — it’s always free.
Our education hub is designed for you and your sales team — perfect for refreshing knowledge or learning new insights that help close more sales. Share this page with your reps to boost their confidence and selling power.
Lab Diamond Value
While some may argue that diamonds should always be expensive to retain their value, it’s essential to remember a fundamental principle of economics: the purchase price alone doesn’t determine an item’s status as an investment or its ability to maintain value.
In fact, any item in this world, be it a diamond, a car, or a piece of art, can become an investment or retain its value if purchased wisely and thoughtfully. It’s not about the initial price tag but rather the inherent qualities, demand, and market dynamics that contribute to an item’s lasting value. Lab-grown diamonds exemplify this concept perfectly. Their affordability compared to earth-mined diamonds doesn’t diminish their potential as a valuable and ethical investment.

In conclusion
whether you’re buying a diamond, a car, or any other item, the key to it retaining or appreciating in value lies in thoughtful selection, quality, and market dynamics, not solely in the purchase price. Lab-grown diamonds are a prime example of how value and ethics can coexist, offering you both a beautiful piece of jewelry and a smart investment in a more sustainable future.

High-Quality Standards
Lab-grown diamonds often exceed the quality standards of mined diamonds in terms of cut, clarity, and color, making them intrinsically valuable.
Evolving Market
The market for lab-grown diamonds is growing, reflecting increased consumer demand for ethical and sustainable options. This trend can lead to potential appreciation in value over time.
Transparency
Lab-grown diamonds come with detailed documentation, providing assurance of their origin and quality. This transparency builds trust and reinforces their value.
Customization
Customization
Lab-grown diamonds offer unique customization options, allowing you to create personalized jewelry pieces. Custom items often hold sentimental and emotional value, which can translate into higher resale value.
How Are
They Made
How Are They Made
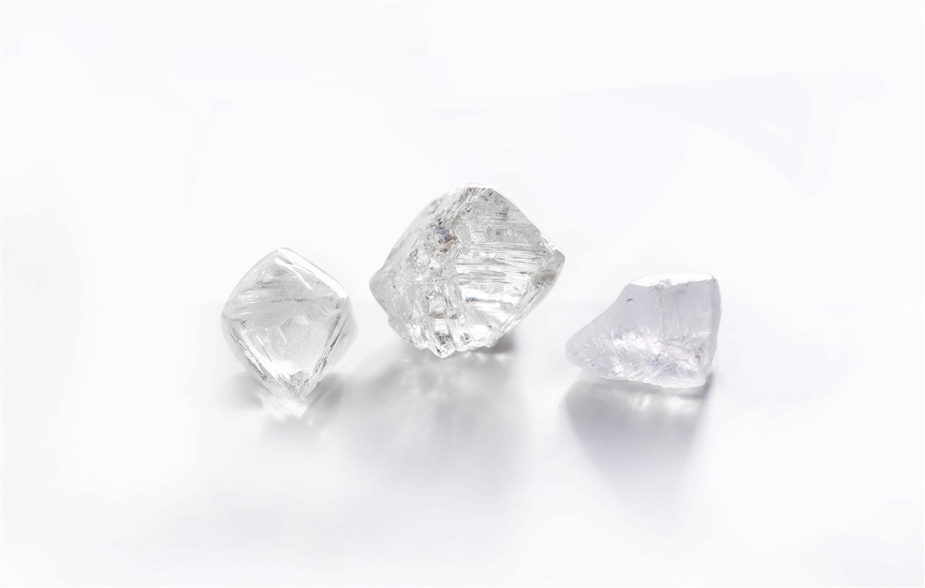

Shoppers are increasingly choosing lab-grown diamonds over mined diamonds for many reasons: they’re more sustainable, more affordable, and provide complete assurance that they were ethically sourced. Lab diamonds are real diamonds that are optically, physically, and chemically identical to their mined counterparts, and will test as a diamond when a diamond tester is used.
There are two processes in which lab diamonds can be grown:
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
- High Pressure, High
- Temperature (HPHT)
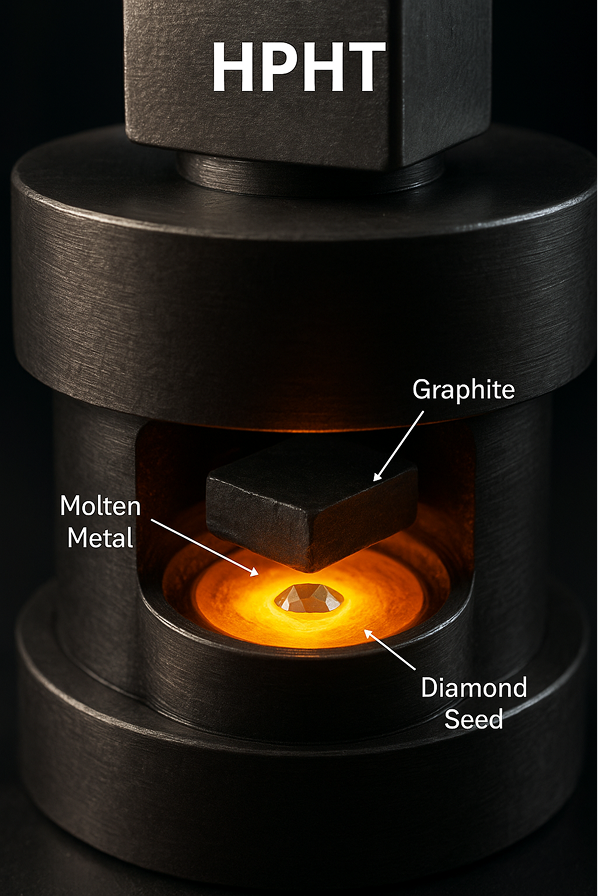
The HPHT method -the original method
To grow an HPHT diamond, a small diamond seed (a very tiny diamond) is placed in carbon, the element that diamonds are made of. The diamond seed is exposed to extreme heat and pressure, replicating the way diamonds are naturally grown underground by the earth. The diamond seed is exposed to temperatures of over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit and pressure of about 1.5 million PSI (pounds per square inch). The carbon melts and forms a diamond around the seed. It is then cooled and the diamond is formed.
A rough HPHT diamond forms differently than a rough CVD diamond.
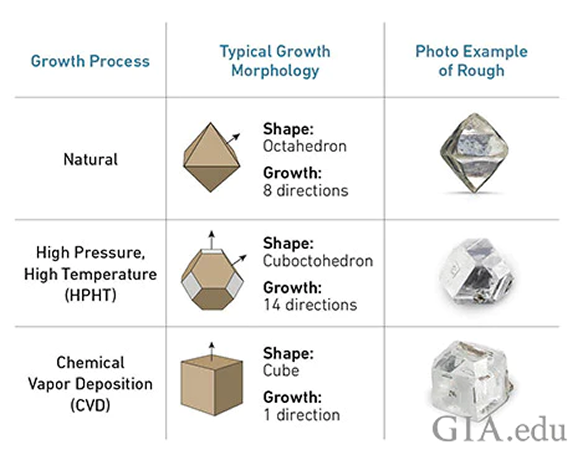
HPHT diamonds are more likely to have a yellowish hue because they are exposed to nitrogen while forming. They also tend to have darker inclusions, which are metallic. These metallic inclusions can help scientists identify them as lab-grown because naturally formed diamonds rarely capture metals during formation.
How Are CVD Diamonds Made
The CVD method was created in the 1980s, making it newer than the HPHT method. The CVD method imitates how diamonds form in interstellar gas clouds. The CVD method uses less pressure than the HPHT method as well as smaller machines.
The CVD method places a diamond seed in a vacuum chamber. This chamber becomes filled with carbon-rich gases and is heated to nearly 1500 degrees Fahrenheit. The gas turns into plasma from these extremely high temperatures, causing the release of carbon pieces. These carbon pieces become layered onto the diamond seed, which grows the diamond

How to Identify HPHT and CVD Diamonds
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Inscriptions: GIA 6441476804, LABORATORY-GROWN
Comments: Additional growth remnant are not shown.
This is a man-made diamond produced by HPTP (High Pressure High Temperature) growth process. No evidence of treatment was detected.
HPHT Diamonds
The most reliable way to identify an HPHT diamond would be to simply look at its grading report. Lab diamond grading reports will specify if the diamond was grown through the HPHT method or the CVD method. Below is an example of a GIA report that identifies a lab diamond as an HPHT diamond.
Another way to identify an HPHT diamond would be to see if it has a blue tint. Some (but not all) HPHT diamonds have what is called a blue nuance, a side effect of the HPHT process. The HPHT process can expose diamonds to boron, which is what can give diamonds a blue color. In fact, fancy blue diamonds are the result of extra boron during the growing process!
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
CVD Diamonds
CVD diamonds have fewer tells. The easiest way to identify if you have a CVD diamond would be to check the diamond’s grading report, which will list how the diamond was grown.
You will not be able to tell the difference between a CVD and HPHT diamond with the naked eye. Both methods can create a beautiful, sparkling diamond. Both the CVD method and the HPHT method will create a real diamond that is optically, chemically, and physically identical to earth-grown diamonds.
Whether CVD or HPHT, we select only the finest lab-grown diamonds — chosen for maximum brilliance, sparkle, and beauty. Every stone is verified to meet our highest standards, so you get diamonds that truly shine.

Diamond Cut:
Diamond cut refers to the way a diamond is fashioned from its raw, rough state into a polished gemstone. It encompasses several elements:
Proportions: The proportions of a diamond, including the angles and dimensions of its facets, are essential for maximizing its brilliance and sparkle. A well-cut diamond allows light to enter and reflect back through the top, creating the dazzling play of light that diamonds are known for.
Symmetry: A symmetrical diamond reflects light more evenly, resulting in enhanced sparkle. Imperfections in symmetry can lead to a less vibrant appearance.
Facets: The number and arrangement of facets on a diamond’s surface affect how it interacts with light. Facets are like tiny mirrors that bounce light within the stone, producing the scintillation and fire that are characteristic of diamonds.
Reflective Qualities: The quality of a diamond’s polish on its facets determines how efficiently light can pass through and be refracted. A well-polished diamond will exhibit maximum brilliance.

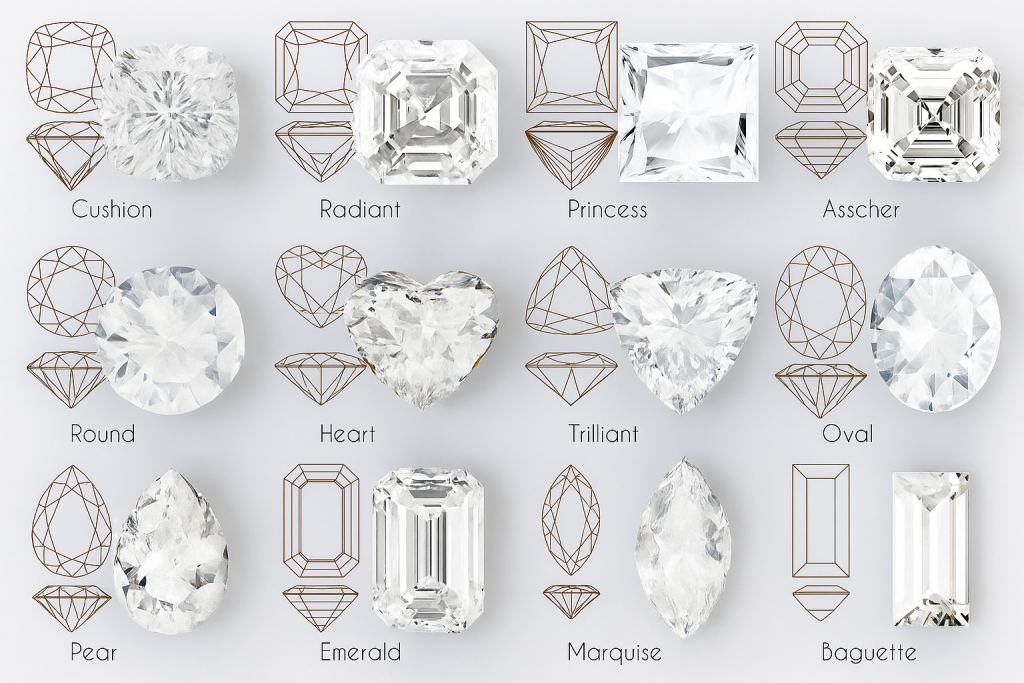
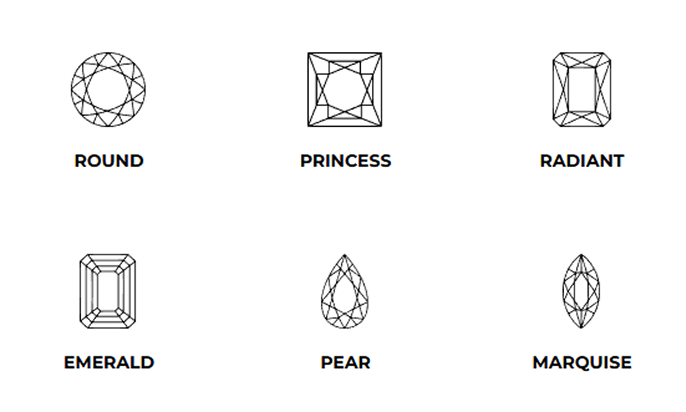
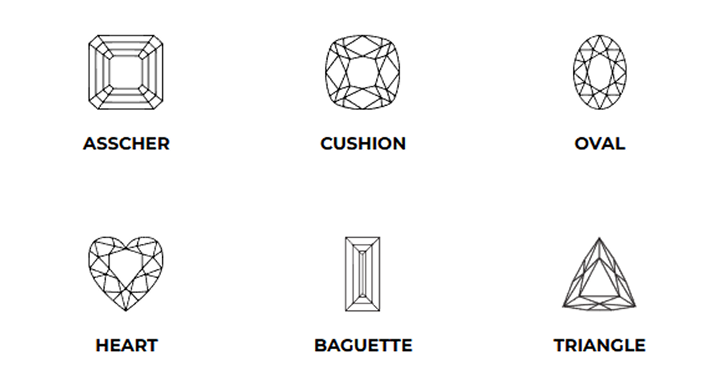
Diamond Shape:
Diamond shape, on the other hand, pertains to the external outline or silhouette of the diamond when viewed from above. There are several popular diamond shapes, each with its own unique charm:
Round Brilliant Cut: The round shape is the most classic and popular choice. It boasts 57 or 58 facets, making it exceptionally brilliant and lively.
Princess Cut: Known for its sharp, square or rectangular shape, the princess cut is a modern and elegant choice, with pointed corners and plenty of sparkle.
Emerald Cut: Featuring rectangular facets and step-cut sides, the emerald cut is renowned for its timeless and sophisticated appearance, emphasizing clarity and the natural beauty of the diamond.
Cushion Cut: This square or rectangular shape with rounded corners offers a vintage and romantic look, known for its soft, pillow-like appearance.
Asscher Cut: Similar to the emerald cut but square in shape, the asscher cut is celebrated for its Art Deco charm and elegant symmetry.
Pear Cut: Resembling a teardrop, the pear cut combines the round brilliance of the top with a tapering, pointed end, offering a unique and graceful appearance.
Heart Cut: Symbolic of love, the heart-shaped diamond is distinctive and romantic, making it a popular choice for sentimental jewelry.
Oval Cut: The oval shape offers the brilliance of the round cut with an elongated, flattering appearance on the finger.
Marquise Cut: Known for its boat-like shape with pointed ends, the marquise cut creates an illusion of greater size and elegance.
Radiant Cut: Combining the elegance of the emerald cut with the brilliance of the round cut, the radiant cut is a square or rectangular shape with cropped corners, offering dazzling sparkle
Diamond Carat
In addition to cut and shape, diamonds are also evaluated based on size (carat weight) and clarity (the presence of internal or external imperfections). These characteristics, along with cut and shape, collectively influence the overall beauty and value of a diamond, making it essential for consumers to carefully consider their preferences and priorities when selecting the perfect diamond for their jewelry.

Diamond Carat
Carat refers to the weight of a diamond, not its size, though the two are often linked. One carat equals 0.2 grams, and diamonds are measured to the hundredth of a carat for precision. While a higher carat weight generally means a larger stone, two diamonds of the same carat can look different depending on their cut and shape.
Carat weight has a significant impact on a diamond’s value and presence, but bigger is not always better. A well-cut diamond of a lower carat can often appear just as stunning as a heavier stone. When choosing the right diamond, it’s important for buyers to balance carat with clarity, cut, and shape to get the best beauty and value within their budget.
Lab-grown diamonds often show superior clarity and brilliance compared to mined diamonds. Because they are created in controlled environments, most lab diamonds are produced with fewer impurities and inclusions, giving them higher average clarity grades. Many lab-grown stones fall in the VS (Very Slightly Included) to VVS (Very Very Slightly Included) range, which means they appear eye-clean and deliver exceptional sparkle. This consistency allows jewelers and buyers to access high-quality diamonds with remarkable shine and brilliance — often at a more affordable price than natural stones of similar grade.
Diamond Clarity
Clarity refers to how clean a diamond is from internal features (inclusions) and external marks (blemishes). The fewer the inclusions, the rarer and more valuable the stone.
The GIA clarity scale is the global standard, ranging from Flawless (FL) — no visible inclusions under 10x magnification — to Included (I1–I3), where inclusions are visible to the naked eye.
FL / IF (Flawless / Internally Flawless): No inclusions visible at 10x. Extremely rare.
VVS1 – VVS2 (Very Very Slightly Included): Minute inclusions, very hard to see even for an expert.
VS1 – VS2 (Very Slightly Included): Minor inclusions, still invisible to the eye. Excellent balance of beauty and value.
SI1 – SI2 (Slightly Included): Inclusions visible under 10x, sometimes visible to the eye depending on size/placement.
I1 – I3 (Included): Inclusions easily visible. Least expensive clarity grades.
Size Chart By Shape
Contact Us
Our team is here to help with any questions about our lab-grown diamonds, custom jewelry, or your order. Simply fill out the form below and we’ll get back to you ASAP.










